B21, China Town Mall, Midrand
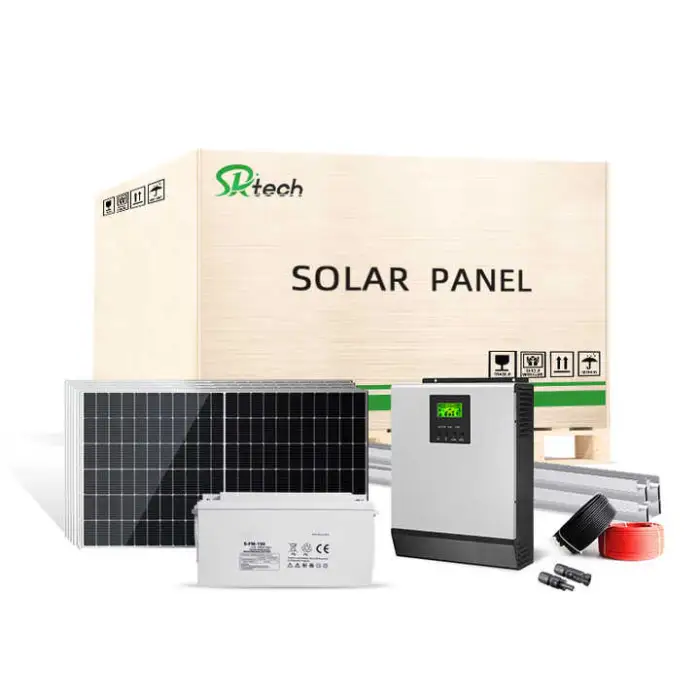
Complete Set Solar Energy Power Storage System 5000W 3KW 6KW 8KW 10KW Hybrid Solar Panel Electric Power Generation Kit
- Section : Electrical & Tools
- Category : Solar Energy System
- SKU : 1600988709451

- Shipping Timeframes: All orders are processed within 2-5 business days (excluding weekends and holidays). After your order has been processed, the estimated delivery time is before 05 May, 2026, depending on customs, Please note that due to high demand, some items may experience longer shipping times, which will be communicated at order confirmation email.
- Order Processing Time: Please allow 2-5 business days for us to process your order before it is shipped . Orders placed after 16:00 on Fridays, or during weekends and public holidays, will begin processing on the next business day. Processing times may be extended during peak seasons or sales events.
- Manufacturing Time: Some products needs manufacturing time, the manufacturing process will take approximately 10-30 business days depending on the product. This timeframe may vary depending on the complexity of the product and current demand. but this will be communicated with you during order confirmation.
- Returns and Exchanges: We offer a 30-day return policy for most items. If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, you may return it within 30 days of receipt for a refund or exchange. Items must be unused, in their original packaging, and accompanied by proof of purchase. Return shipping costs are the responsibility of the customer, unless the item was damaged or defective upon arrival.
1. What power sizes does this Complete Set Solar Energy Power Storage System come in?
The system is available in multiple power options ranging from 3 kW up to 15 kW. Common configurations include 3 kW, 5 kW (5000 W), 6 kW, 8 kW, 10 kW and 15 kW — confirm the exact SKU and components when ordering.
2. What does 'hybrid' mean in this product name?
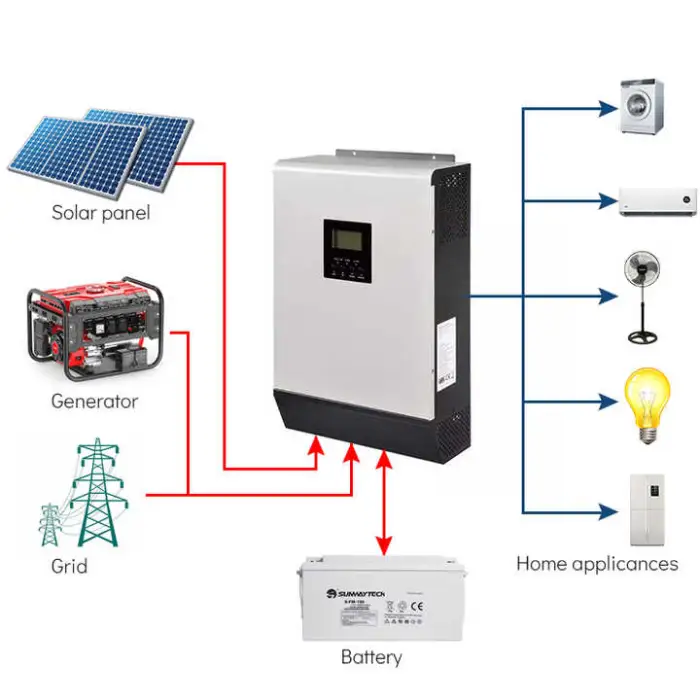
Here, 'hybrid' refers to an integrated solution combining solar panels, battery storage and control electronics so the system can generate, store and supply power. Note: the listed inverter is an off-grid type; if you need a grid-interactive hybrid (grid-tie plus storage), verify that option with the seller.
3. Is this an off-grid or grid-tied system?
The specification lists this as an off-grid system with an off-grid inverter. If you require a grid-tied or grid-interactive configuration, contact the supplier to confirm availability or to order a different inverter that supports grid-connection and export.
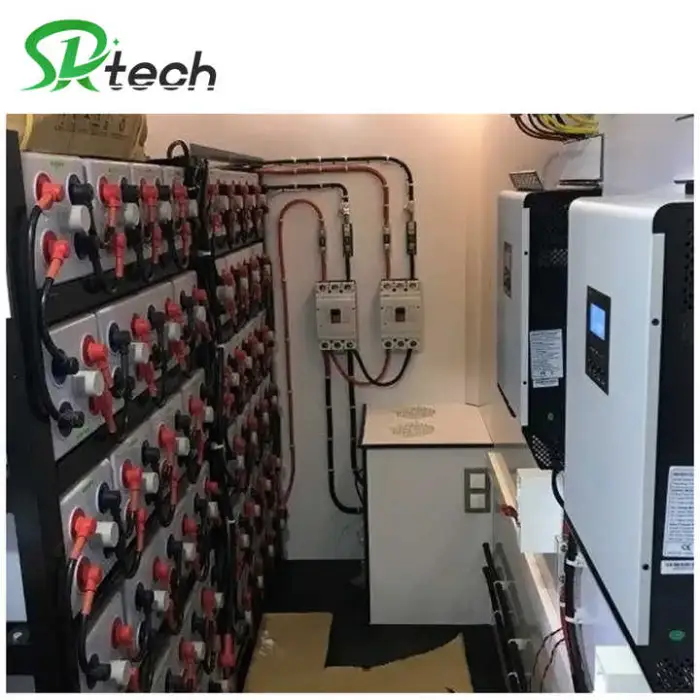
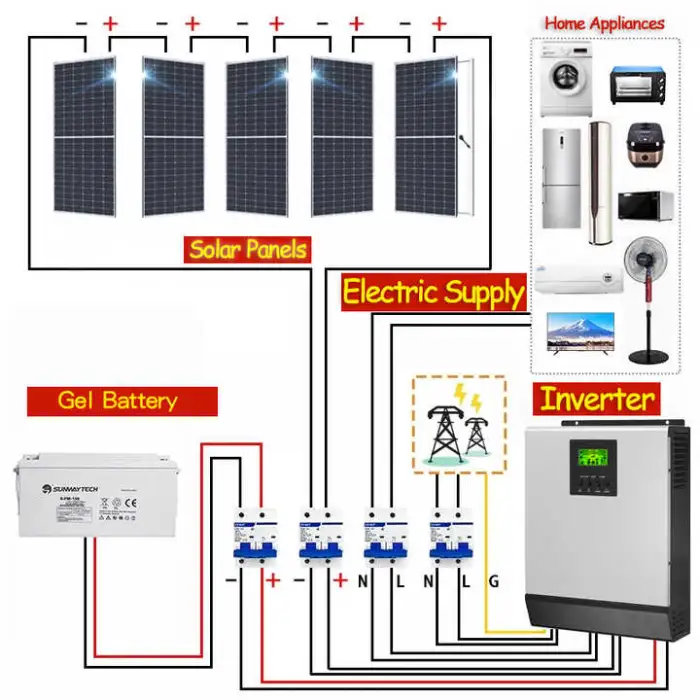
4. What components are included in the complete kit?
Typical kits include solar panels (monocrystalline or polycrystalline), charge controller (MPPT or PWM), battery bank (lead-acid or lithium-ion depending on selection), off-grid inverter, mounting hardware and basic cabling. Exact contents vary by package — always check the product packing list before purchase.
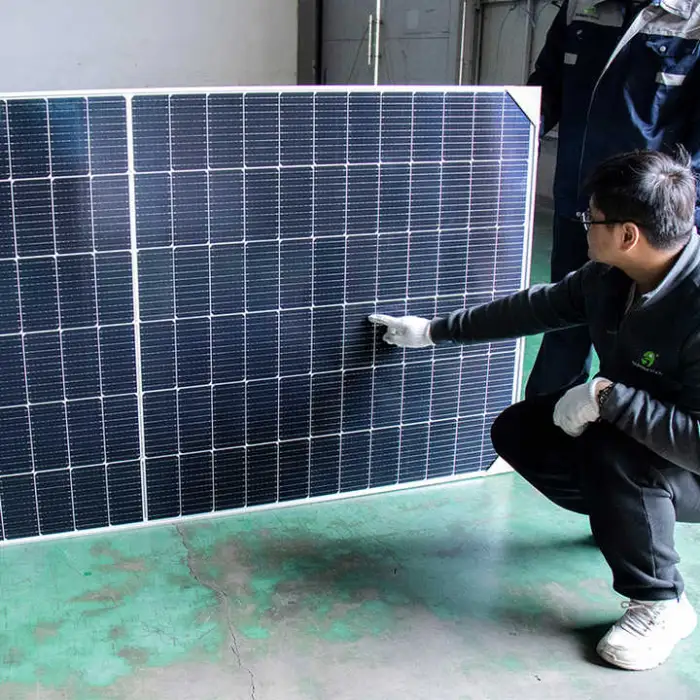
5. What types of solar panels and batteries are supported?
Solar panels: monocrystalline silicon and polycrystalline silicon options. Batteries: lead-acid (flooded/gel/AGM depending on kit) or lithium-ion. Choose based on budget, space and desired cycle life.
6. What is the difference between MPPT and PWM controllers, and which should I choose?
MPPT controllers are more efficient (especially in variable light or with higher-voltage arrays) and extract more energy from the panels. PWM controllers are simpler and cheaper. For most modern systems and larger arrays, MPPT is recommended.
7. What output voltage does the system provide?
The system output voltage is specified as 220–240 V (typical for single-phase residential applications). Confirm phase configuration (single or three-phase) for larger installations.
8. How long will the system power my home or appliances?
Runtime depends on battery capacity (kWh) and your load (kW). Use: Runtime (hours) = Battery capacity (kWh) ÷ Load (kW). Example: a 10 kWh battery powering a 2 kW load lasts about 5 hours (ignoring losses). Check inverter continuous and surge ratings for appliances with high starting currents.
9. Can I expand the system later (more panels or batteries)?
Most kits are expandable, but expansion must respect inverter, charge controller and battery bank limits. Always verify maximum PV array size, battery capacity and system compatibility with the supplier or installer before adding components.
10. How long does it take to charge the batteries from the solar panels?
Charging time depends on battery capacity, available solar power and controller limits. Estimate: Charge time (hours) ≈ Battery capacity (kWh) ÷ Effective solar charging power (kW), accounting for ~10–20% charging losses. Example: 10 kWh battery with 2 kW effective charging power ≈ 5–6 hours of good sun.
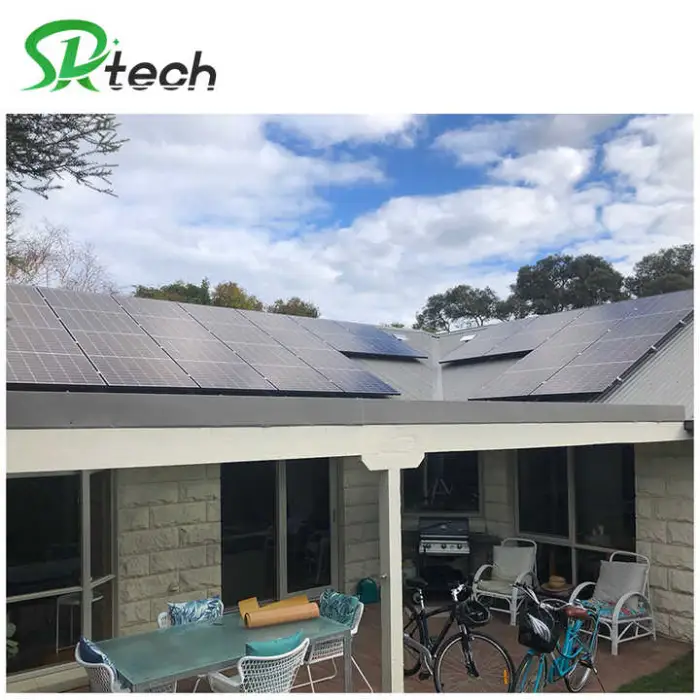
11. What installation requirements and permits are needed?
Installation options include roof-mount or ground-mount racks. Professional installation by a certified electrician/installer is recommended. Local permits and inspections may be required — check local codes and utility rules before installation.
12. What maintenance is required and what is the expected lifespan?
Maintenance: periodic panel cleaning, battery health checks, inverter/controller firmware and connection inspections. Typical lifespans: solar panels 20+ years (performance warranty varies), lead-acid batteries 3–7 years, lithium batteries 8–15+ years depending on chemistry and cycling. Inverter warranties often range 5–10 years.
13. Can I use this system as backup power during outages?
Yes — off-grid systems and hybrid storage kits are commonly used for backup power. Ensure the system is sized for the critical loads you want to run and that the inverter supports automatic transfer/backup functionality if required.
14. Are there warranties, certifications, and safety approvals for this system?
Warranties and certifications (CE, IEC, UL, etc.) vary by manufacturer and specific components. Ask the seller for documentation on panel performance warranties, inverter warranty, battery warranty and applicable safety/certification records before purchase.
Latest Order Arrivals
Discover our latest orders
12 Heads Embroidery Machine

Dewatering Pump Machine

Order Collection

Portable Water Drilling Rig

Order Usefully Collected

Batch of Orders

Agriculture Processing Machines

Meat Grinder Machine

Water Pump Equipment

Packaging Machine and accessories

Fabrics Manufacturing Equipment

Mining Equipments

Food Processing Machine

Batch of Orders

Batch of Orders

Latest Orders Labelled
wheel alignment machines

new arrivals
Pre Orders Offloading

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

26 January 2026

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper Rewinding Machine

latest arrivals

offloading

order success

order collection

order offloading