B21, China Town Mall, Midrand
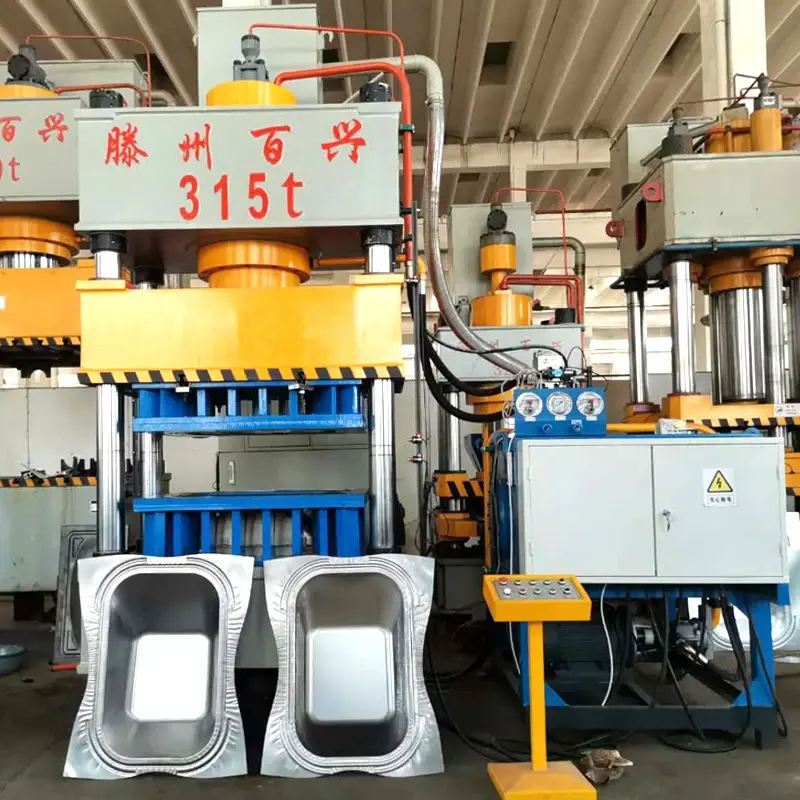
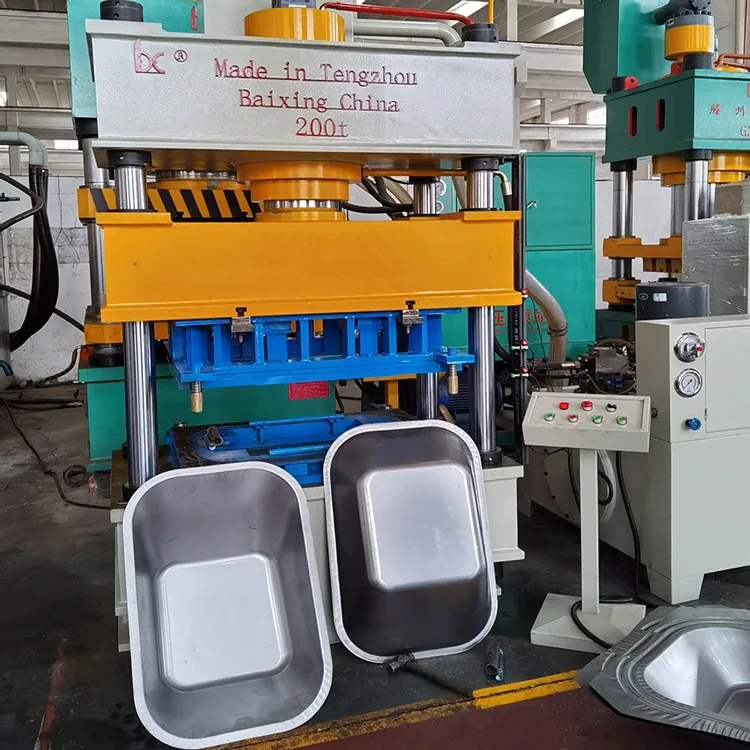
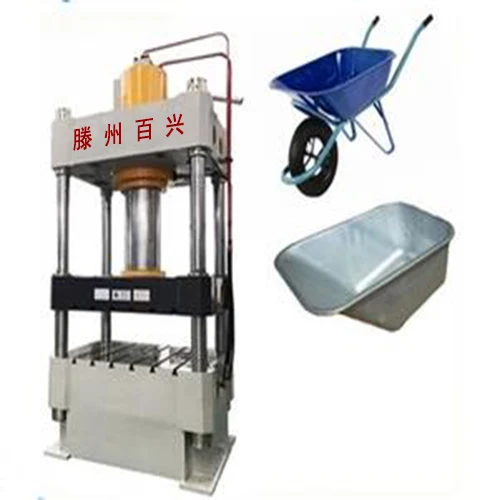
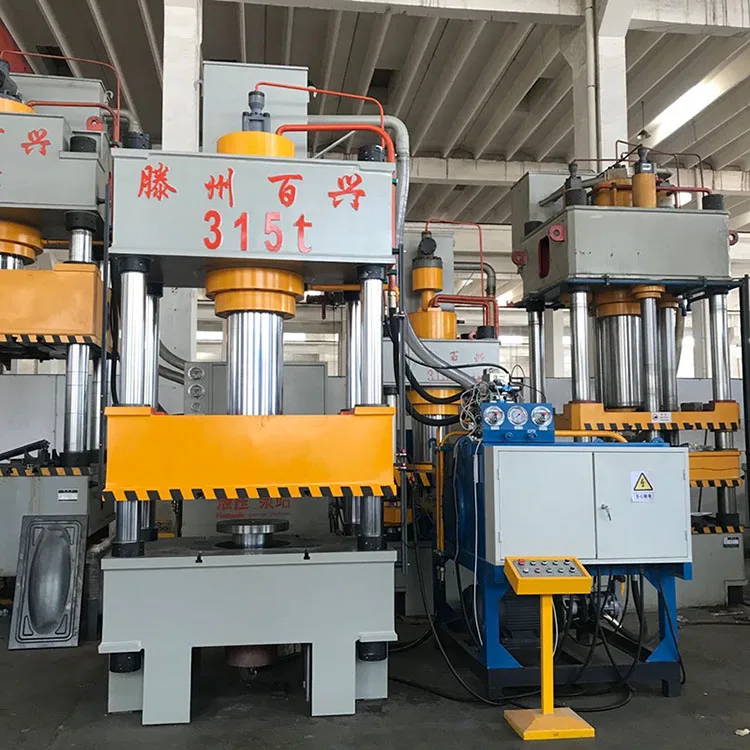
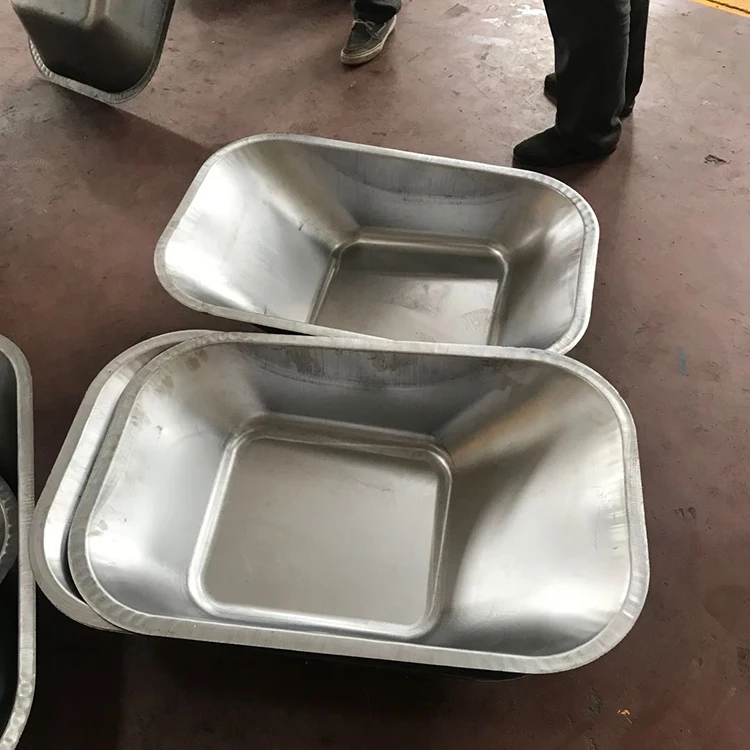
4 column hydraulic press machine wheel barrow making hydraulic press, wheelbarrow pressing machine
- Section : Machinery
- Category : Machine Tool Equipment
- SKU : 1600592655302

- Shipping Timeframes: All orders are processed within 2-5 business days (excluding weekends and holidays). After your order has been processed, the estimated delivery time is before 04 May, 2026, depending on customs, Please note that due to high demand, some items may experience longer shipping times, which will be communicated at order confirmation email.
- Order Processing Time: Please allow 2-5 business days for us to process your order before it is shipped . Orders placed after 16:00 on Fridays, or during weekends and public holidays, will begin processing on the next business day. Processing times may be extended during peak seasons or sales events.
- Manufacturing Time: Some products needs manufacturing time, the manufacturing process will take approximately 10-30 business days depending on the product. This timeframe may vary depending on the complexity of the product and current demand. but this will be communicated with you during order confirmation.
- Returns and Exchanges: We offer a 30-day return policy for most items. If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, you may return it within 30 days of receipt for a refund or exchange. Items must be unused, in their original packaging, and accompanied by proof of purchase. Return shipping costs are the responsibility of the customer, unless the item was damaged or defective upon arrival.
1. What is the nominal capacity of this 4-column hydraulic press?
The press has a nominal capacity of 3150 kN (approximately 315 tons), suitable for heavy forming tasks such as wheelbarrow tray pressing.
2. What is the ejection (ejector) nominal force?
The ejector (ejection) nominal force is 400 kN, used for part release or secondary forming operations.
3. What is the working hydraulic pressure of the machine?
The working pressure is 25 MPa (megapascals).
4. What are the stroke and travel dimensions?
Master cylinder effective stroke: 800 mm. Ejector stroke: 300 mm. Maximum opening height: 1250 mm. Minimum shut height: 100 mm.
5. What is the effective working table area?
The effective table dimensions are 1600 mm left-to-right (L/R) by 1200 mm front-to-back (F/B).
6. What are the machine speeds (approach, working and return)?
Rapid down (approach) speed: 120 mm/s. Working (pressing) speed: 5–10 mm/s. Return speed: 90 mm/s.
7. What is the motor power requirement?
The hydraulic power unit uses an 18.5 kW motor. Electrical specification (voltage/phase) should be confirmed with the supplier for your region.
8. Is this press suitable specifically for wheelbarrow manufacturing?
Yes. The press is designed for wheelbarrow making and similar sheet metal forming tasks, providing the force, stroke and table size needed for tray forming and related operations.
9. What tooling or dies are required for wheelbarrow pressing?
Custom forming dies and male/female molds are required and should be designed to match the press stroke, table area and part geometry. The supplier or a die maker can design and supply tooling.
10. What safety features should be present or can be expected?
Typical safety features include emergency stop, safety guards or light curtains, overload/overpressure protection valves, and interlocks. Exact safety fittings should be confirmed with the manufacturer or installer.
11. What are the installation and foundation requirements?
The press requires a stable concrete foundation with anchor bolts and proper leveling. Exact foundation drawings, bolt pattern and weight/load data should be requested from the supplier prior to installation.
12. What hydraulic oil should be used and how often should it be changed?
Use hydraulic oil that meets the manufacturer's specification (commonly ISO VG46 in similar presses). Change intervals depend on operating hours and contamination but typically every 1,000–2,000 hours or per the supplier's maintenance schedule.
13. What is the expected cycle time?
Cycle time depends on stroke length, tooling and operator sequence. Typical cycle times for forming operations on this type/size of press are roughly 15–45 seconds per cycle; actual times should be validated in production.
14. Can this press be customized (different strokes, table sizes, controls)?
Yes. Many manufacturers offer customization such as altered stroke lengths, table sizes, additional sensors, PLC/HMI controls or special hydraulic circuits. Discuss required modifications with the supplier.
15. What maintenance and service support should I plan for?
Regular maintenance includes hydraulic oil and filter changes, inspection of seals and hoses, lubrication of moving parts, checking alignment and fasteners, and periodic hydraulic system checks. Arrange local service support and spare parts (seals, valves, filters) with the supplier.
Latest Order Arrivals
Discover our latest orders
12 Heads Embroidery Machine

Dewatering Pump Machine

Order Collection

Portable Water Drilling Rig

Order Usefully Collected

Batch of Orders

Agriculture Processing Machines

Meat Grinder Machine

Water Pump Equipment

Packaging Machine and accessories

Fabrics Manufacturing Equipment

Mining Equipments

Food Processing Machine

Batch of Orders

Batch of Orders

Latest Orders Labelled
wheel alignment machines

new arrivals
Pre Orders Offloading

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

26 January 2026

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper Rewinding Machine

latest arrivals

offloading

order success

order collection

order offloading