B21, China Town Mall, Midrand
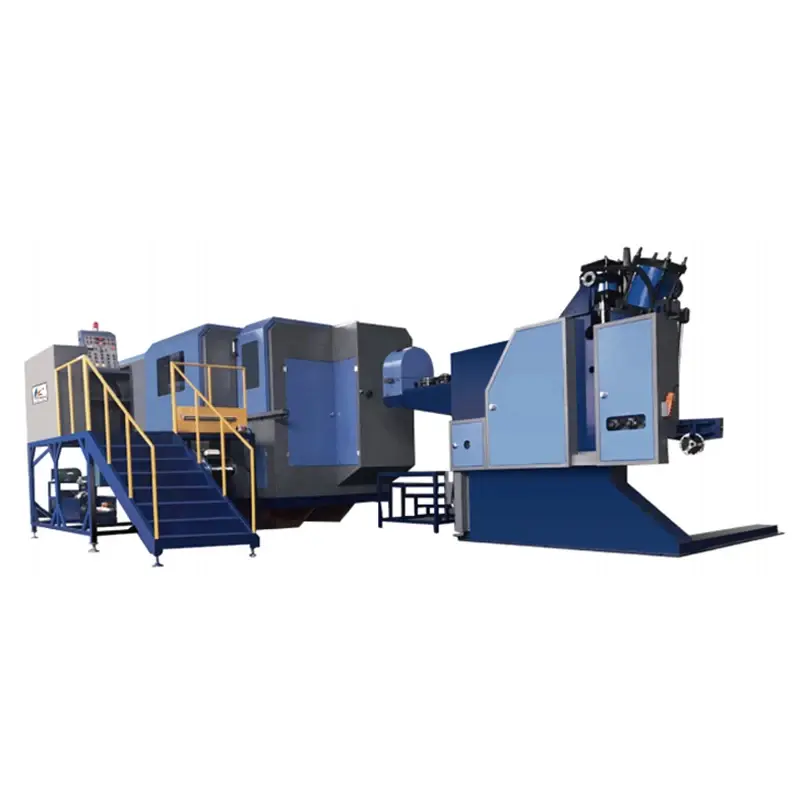
Automatic Cold Forging Bolt Nut Making Machine
- Section : Machinery
- Category : Metal & Metallurgy Machinery
- SKU : 60737488055

- Shipping Timeframes: All orders are processed within 2-5 business days (excluding weekends and holidays). After your order has been processed, the estimated delivery time is before 05 May, 2026, depending on customs, Please note that due to high demand, some items may experience longer shipping times, which will be communicated at order confirmation email.
- Order Processing Time: Please allow 2-5 business days for us to process your order before it is shipped . Orders placed after 16:00 on Fridays, or during weekends and public holidays, will begin processing on the next business day. Processing times may be extended during peak seasons or sales events.
- Manufacturing Time: Some products needs manufacturing time, the manufacturing process will take approximately 10-30 business days depending on the product. This timeframe may vary depending on the complexity of the product and current demand. but this will be communicated with you during order confirmation.
- Returns and Exchanges: We offer a 30-day return policy for most items. If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, you may return it within 30 days of receipt for a refund or exchange. Items must be unused, in their original packaging, and accompanied by proof of purchase. Return shipping costs are the responsibility of the customer, unless the item was damaged or defective upon arrival.
1. What models are available for the Automatic Cold Forging Bolt Nut Making Machine?
Two models are listed: RBF-84S and RBF-134L.
2. What is the forging force for each model?
Forging force is 60,000 (RBF-84S) and 120,000 (RBF-134L) as shown in the specification sheet.
3. What bolt diameters can the machines produce?
Applicable bolt diameter range is 5 mm to 28 mm (applies to the machine family as specified).
4. What is the maximum output (production speed) for each model?
Maximum output is 120–180 pcs/min for RBF-84S and 75–110 pcs/min for RBF-134L, depending on part geometry and process parameters.
5. What are the maximum cut-off diameter and cut-off length for each model?
Max cut-off diameter: 10 mm (RBF-84S) and 15 mm (RBF-134L). Max cut-off length: 115 mm (RBF-84S) and 190 mm (RBF-134L).
6. What blank (shank) lengths can the machines accept?
Shank length of blank range is 15–90 mm for RBF-84S and 20–160 mm for RBF-134L.
7. What are the main ram stroke and main motor power for each model?
Main ram stroke: 160 mm (RBF-84S) and 270 mm (RBF-134L). Main motor power: 22 (RBF-84S) and 37 (RBF-134L) as specified (confirm units with manufacturer).
8. What are the die pitch and die dimensions provided in the specs?
Die pitch: 70 mm (RBF-84S) and 110 mm (RBF-134L). Overall dimensions listed: cut-off die ~50×50L (RBF-84S) and 63×69L (RBF-134L); punch die ~45×125L (RBF-84S) and 60×130L (RBF-134L); main die ~60×130L (RBF-84S) and 86×190L (RBF-134L).
9. Which materials can be cold forged on this machine?
Typical materials for cold forging include low- and medium-carbon steels, stainless steels, brass, copper and some aluminum alloys. Final suitability depends on material ductility and hardness; consult the manufacturer with specific material grades.
10. How many forging stations does each model have?
The specification indicates forging station counts relative to each model; please confirm with the manufacturer or sales sheet for the exact station layout for RBF-84S and RBF-134L.
11. What factory utilities and installation requirements are needed?
Required utilities typically include appropriate electrical supply (matching the main motor rating), compressed air and stable foundation/anchoring. Exact requirements (voltage, phase, air pressure, power factor) should be confirmed with the supplier before installation.
12. What tooling and changeover options are available?
The machine uses dedicated cut-off, punch and main dies specified in the datasheet. Tooling changeover time depends on the tooling set and operator skill; quick-change tooling options or fixture assistance may be available—ask the vendor about custom tooling and spares kits.
13. What maintenance and service are recommended?
Regular maintenance includes lubrication of moving parts, periodic inspection and replacement of wear parts (dies, punches, guides), hydraulic/electrical system checks, and alignment verification. Follow the manufacturer's maintenance schedule for intervals and procedures.
14. What safety features should I expect and what operator training is required?
Expect standard guarding, emergency stop, safety interlocks and possibly light curtains or two-hand controls depending on configuration. Operator training on safe operation, lockout/tagout, basic troubleshooting and die change procedures is recommended and may be provided by the manufacturer or distributor.
Latest Order Arrivals
Discover our latest orders
12 Heads Embroidery Machine

Dewatering Pump Machine

Order Collection

Portable Water Drilling Rig

Order Usefully Collected

Batch of Orders

Agriculture Processing Machines

Meat Grinder Machine

Water Pump Equipment

Packaging Machine and accessories

Fabrics Manufacturing Equipment

Mining Equipments

Food Processing Machine

Batch of Orders

Batch of Orders

Latest Orders Labelled
wheel alignment machines

new arrivals
Pre Orders Offloading

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

26 January 2026

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper Rewinding Machine

latest arrivals

offloading
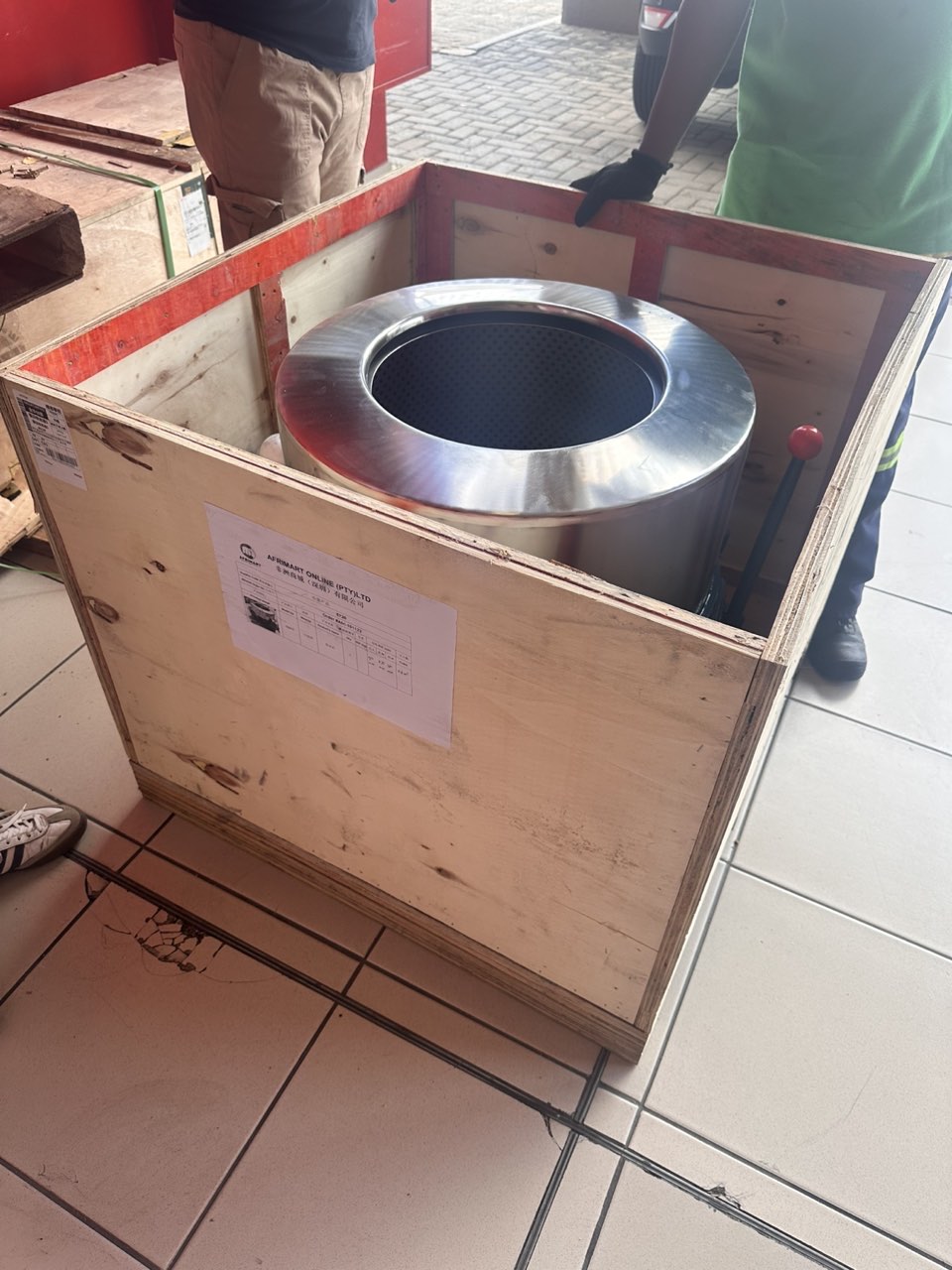

order success

order collection

order offloading




















