B21, China Town Mall, Midrand
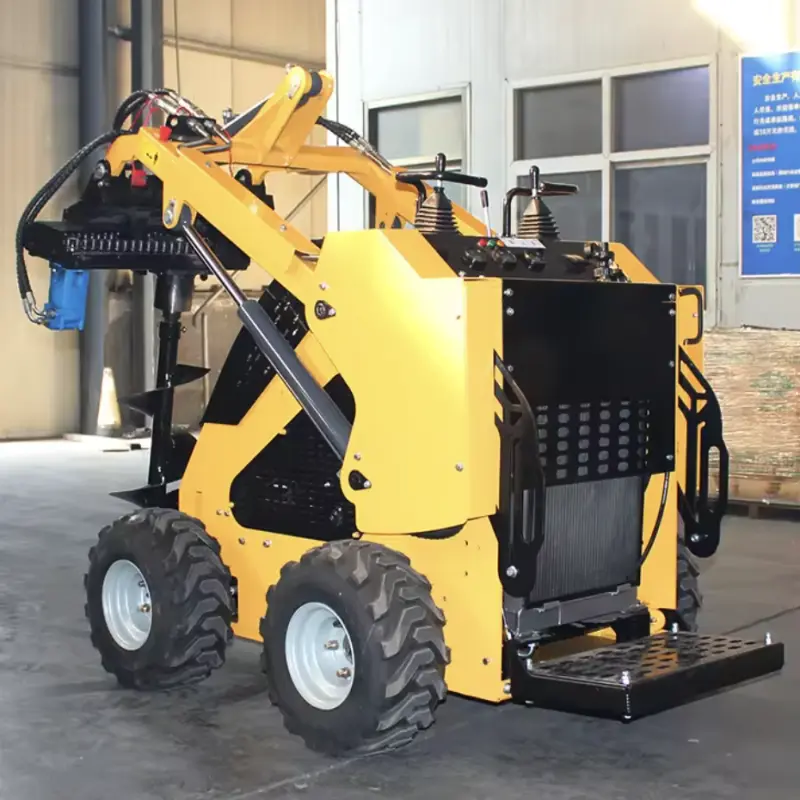
Wheel Loader Skid Steer Diesel Loader
- Section : Machinery
- Category : Engineering & Construction Machinery
- SKU : 1601032375769

- Shipping Timeframes: All orders are processed within 2-5 business days (excluding weekends and holidays). After your order has been processed, the estimated delivery time is before 05 May, 2026, depending on customs, Please note that due to high demand, some items may experience longer shipping times, which will be communicated at order confirmation email.
- Order Processing Time: Please allow 2-5 business days for us to process your order before it is shipped . Orders placed after 16:00 on Fridays, or during weekends and public holidays, will begin processing on the next business day. Processing times may be extended during peak seasons or sales events.
- Manufacturing Time: Some products needs manufacturing time, the manufacturing process will take approximately 10-30 business days depending on the product. This timeframe may vary depending on the complexity of the product and current demand. but this will be communicated with you during order confirmation.
- Returns and Exchanges: We offer a 30-day return policy for most items. If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, you may return it within 30 days of receipt for a refund or exchange. Items must be unused, in their original packaging, and accompanied by proof of purchase. Return shipping costs are the responsibility of the customer, unless the item was damaged or defective upon arrival.
1. What is a Wheel Loader Skid Steer Diesel Loader?
A compact, versatile machine that combines skid-steer maneuverability with a wheel loader configuration, powered by a diesel EPA-compliant engine. It is used for excavation, material handling, landscaping, and other tasks in tight spaces.
2. What kinds of attachments are available for this skid steer?
Common attachments include general-purpose buckets, multi-purpose buckets, pallet forks, hydraulic breakers, augers, trenchers, grapples, brush cutters, and backhoe attachments. Compatibility depends on the quick-coupler system and hydraulic flow of the specific model.
3. Is the engine EPA-compliant?
Yes — the product description indicates an EPA engine. For the exact EPA tier (e.g., Tier 4 Final), verify the specific model's certification with the manufacturer or seller.
4. What fuel does this machine use and what is typical fuel consumption?
It uses diesel fuel. Fuel consumption varies by engine size, workload, and attachment, but small skid steers often consume roughly 1–4 gallons (4–15 L) per hour under typical operating conditions. Ask the seller for model-specific fuel burn rates.
5. How do I choose the right bucket or attachment size?
Match the attachment to the loader's rated operating capacity and hydraulic flow. Consider the material density, desired cycle time, and jobsite access. Consult the attachments guide or dealer to ensure safe loading and machine stability.
6. What are the safety features and recommended safety practices?
Typical features include ROPS/FOPS cab protection, seat belt, backup alarms, and interlocks. Recommended practices: perform pre-shift inspections, use seat belt, operate at safe speeds, avoid overloading, keep bystanders clear, and follow manufacturer safety manuals and training.
7. How often should I perform maintenance and what does it include?
Follow the manufacturer's maintenance schedule. Typical tasks: daily fluid and visual checks, grease fittings, engine oil and filter changes every 100–250 hours (model dependent), hydraulic fluid and filter changes, air filter replacement, and tire checks. Keep records and use genuine parts where possible.
8. Can this skid steer be fitted with a backhoe or front-end loader attachment?
Yes. The product description mentions backhoe and front-end loader capability. Ensure the attachment is rated for the machine's hydraulic flow and lifting capacity and that mounting hardware matches the quick-coupler system.
9. What is the rated operating capacity and lifting height?
Rated operating capacity and lift height vary by model. Smaller mini skid steers typically have a rated capacity from a few hundred to several thousand pounds. Request the specific model spec sheet from the manufacturer or dealer for exact numbers.
10. Are wheel skid steers better than tracked ones?
Wheeled skid steers offer faster travel speeds, lower ground disturbance on hard surfaces, and lower maintenance on some sites. Tracked machines provide better traction and flotation on soft or muddy ground. Choose based on jobsite conditions.
11. How do I transport the machine between job sites?
Use a properly rated trailer or flatbed truck and secure the loader with chains or straps to the designated tie-down points. Check local regulations for transport requirements and consider low loaders for larger models.
12. What tires come standard and are there tire options?
Skid steer wheel loaders commonly come with industrial tread or turf tires. Options often include heavy-duty, puncture-resistant, or foam-filled tires for specific ground conditions. Confirm available tire options with the dealer.
13. Is operator training required or recommended?
Training is strongly recommended and often required by employers or local regulations. Proper training improves safety and productivity and covers controls, attachments, load handling, and daily inspections.
14. What warranty and after-sales support are available?
Warranty terms vary by manufacturer and model. Typical coverage includes a limited warranty on the machine and engine for a set number of hours or months. Ask the seller for full warranty details, service plans, and authorized service centers.
15. How do I get replacement parts and compatible attachments?
Purchase parts through the manufacturer, authorized dealers, or approved parts distributors. Provide the machine serial number and model to ensure correct parts. Aftermarket attachments are available but verify compatibility and safety ratings before use.
Latest Order Arrivals
Discover our latest orders
12 Heads Embroidery Machine

Dewatering Pump Machine

Order Collection

Portable Water Drilling Rig

Order Usefully Collected

Batch of Orders

Agriculture Processing Machines

Meat Grinder Machine

Water Pump Equipment

Packaging Machine and accessories

Fabrics Manufacturing Equipment

Mining Equipments

Food Processing Machine

Batch of Orders

Batch of Orders

Latest Orders Labelled
wheel alignment machines

new arrivals
Pre Orders Offloading

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

26 January 2026

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper Rewinding Machine

latest arrivals

offloading

order success

order collection

order offloading

















