B21, China Town Mall, Midrand
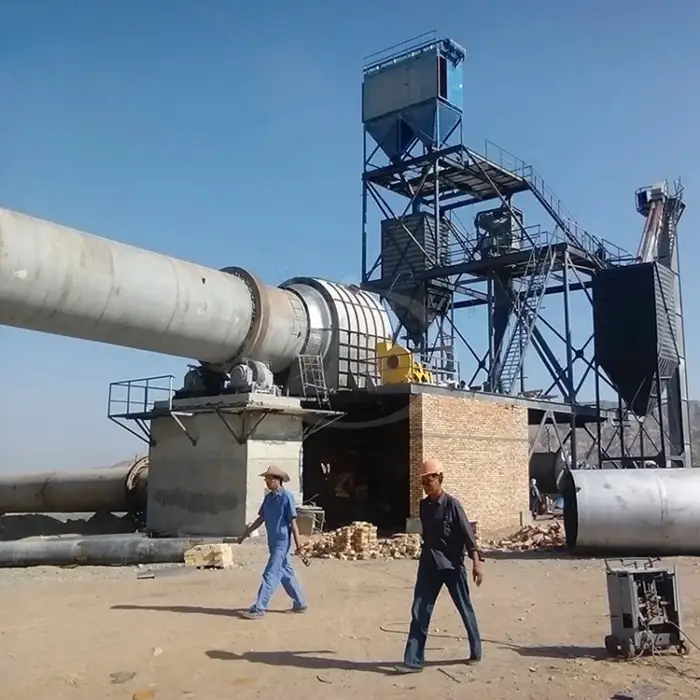
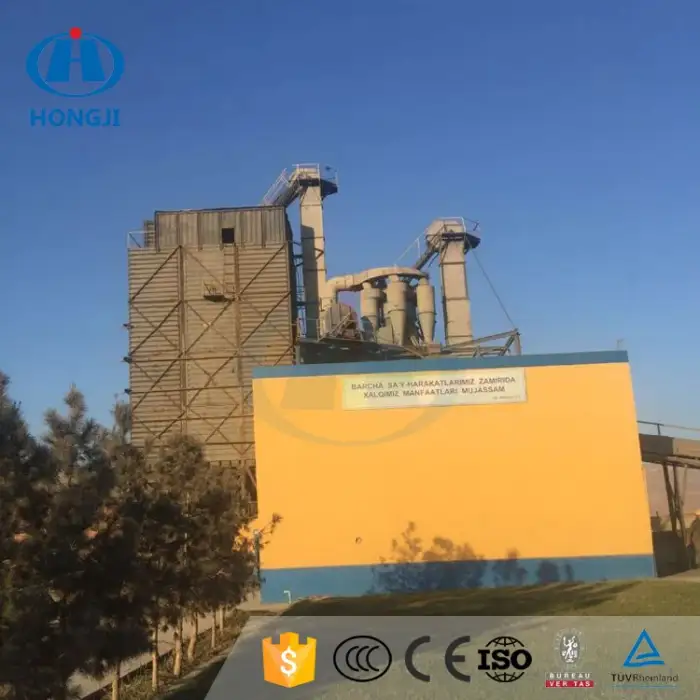
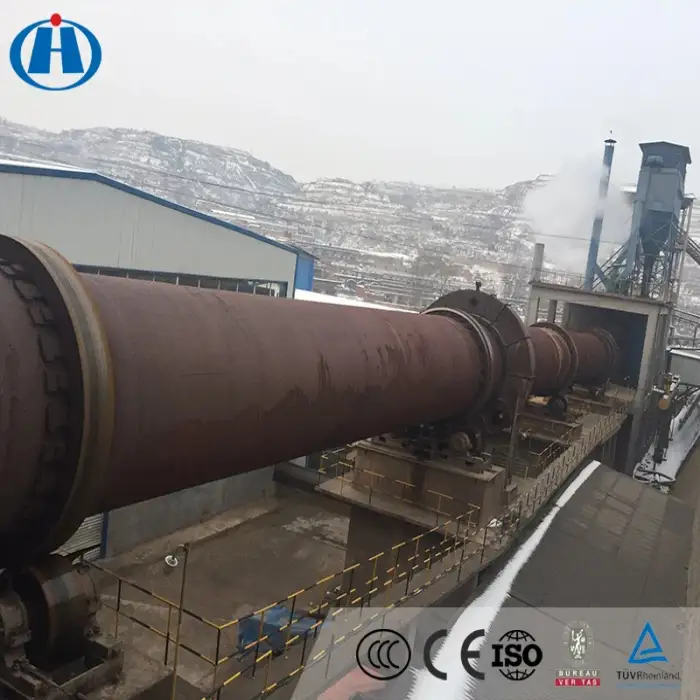
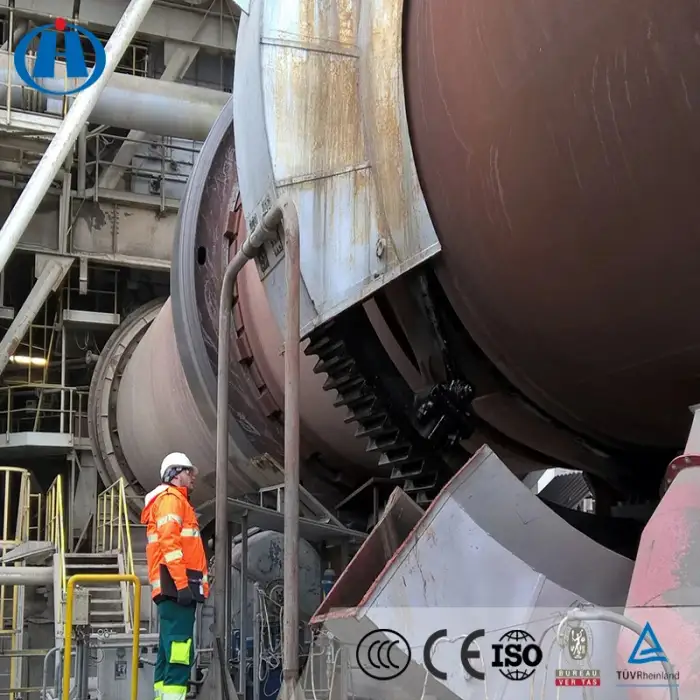
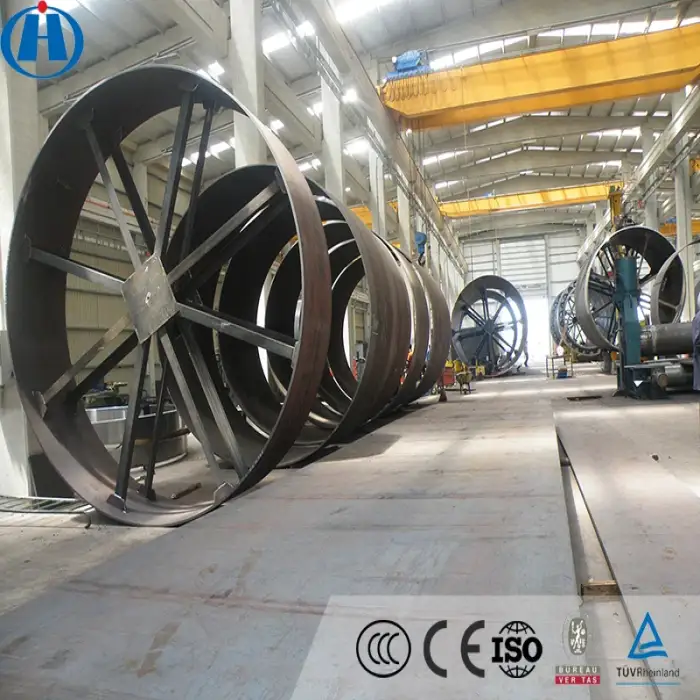
Coal mining machinery high efficient calcine bauxite rotary kiln machine
- Section : Machinery
- Category : Mining Machinery
- SKU : 60746184031

- Shipping Timeframes: All orders are processed within 2-5 business days (excluding weekends and holidays). After your order has been processed, the estimated delivery time is before 08 May, 2026, depending on customs, Please note that due to high demand, some items may experience longer shipping times, which will be communicated at order confirmation email.
- Order Processing Time: Please allow 2-5 business days for us to process your order before it is shipped . Orders placed after 16:00 on Fridays, or during weekends and public holidays, will begin processing on the next business day. Processing times may be extended during peak seasons or sales events.
- Manufacturing Time: Some products needs manufacturing time, the manufacturing process will take approximately 10-30 business days depending on the product. This timeframe may vary depending on the complexity of the product and current demand. but this will be communicated with you during order confirmation.
- Returns and Exchanges: We offer a 30-day return policy for most items. If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, you may return it within 30 days of receipt for a refund or exchange. Items must be unused, in their original packaging, and accompanied by proof of purchase. Return shipping costs are the responsibility of the customer, unless the item was damaged or defective upon arrival.
1. What is a rotary kiln?
A rotary kiln is a cylindrical vessel that is inclined slightly to the horizontal and rotates slowly around its axis. It is used for processing various materials, such as cement, metallurgy, and lime.
2. What materials can be processed in the rotary kiln?
The rotary kiln can process materials like cement clinker, poor iron ore, chrome and nickel, high-alumina mine, chamotte, alumina, chrome ore, and active lime.
3. How does the rotary kiln work?
As the kiln rotates, materials are fed into the upper end and gradually move towards the lower end. Hot gases pass along the kiln, either co-currently or counter-currently, facilitating the heating and processing of materials.
4. What types of kilns are there?
There are several types of kilns, including cement kilns, metallurgy chemical kilns, and lime kilns, each designed for specific materials and processes.
5. What is the difference between dry and wet methods in cement kilns?
The dry method involves feeding dry materials into the kiln, while the wet method involves using a slurry of materials. The choice depends on the desired end product and specific operational requirements.
6. What fuels can be used in the rotary kiln?
Fuels such as gas, oil, or pulverized coal can be used to generate the hot gases required for processing materials in the rotary kiln.
7. What are the applications of a lime kiln?
Lime kilns are primarily used for roasting active lime in steelworks, ferroalloy plants, and for light roasting dolomite.
8. Is the rotary kiln suitable for small-scale operations?
The rotary kiln can be designed for various scales, but its efficiency and suitability for small-scale operations depend on the specific requirements and throughput of the operation.
9. What are the key benefits of using a high-efficient rotary kiln?
High-efficient rotary kilns provide better fuel consumption, improved processing times, and enhanced product quality, leading to lower operational costs and higher productivity.
10. Can the rotary kiln handle different types of materials simultaneously?
While it is possible to process different materials, it is generally recommended to operate with homogenous materials to achieve optimal results and prevent contamination.
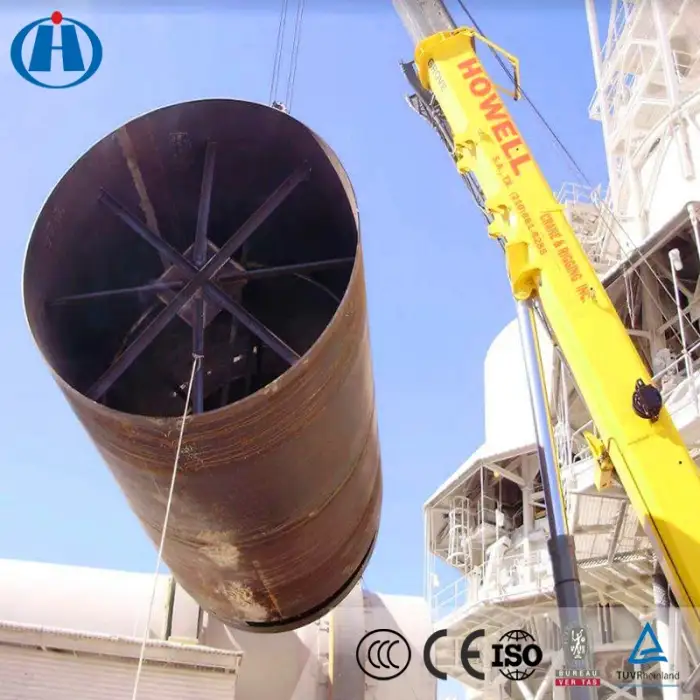
11. What is the role of the burner-pipe in the rotary kiln?
The burner-pipe, or firing pipe, is responsible for projecting a flame inside the kiln, which generates the necessary heat for the processing of materials.
12. How is the rotary kiln maintained?
Regular maintenance includes checking for wear and tear, ensuring proper alignment, inspecting the burner, and cleaning the kiln to prevent buildup that can affect performance.
13. What is the installation process for the rotary kiln?
Installation involves assembling the kiln components, ensuring proper alignment, connecting the fuel and electrical systems, and conducting tests to ensure operational efficiency.
14. What safety measures should be taken when operating a rotary kiln?
Safety measures include proper training for operators, regular inspections, monitoring of emissions, and ensuring that safety equipment is readily available.
15. Where can I find installation examples of the rotary kiln?
Installation examples and showcase sites can usually be found on the manufacturer's website or by contacting their customer service for case studies and references.
Latest Order Arrivals
Discover our latest orders
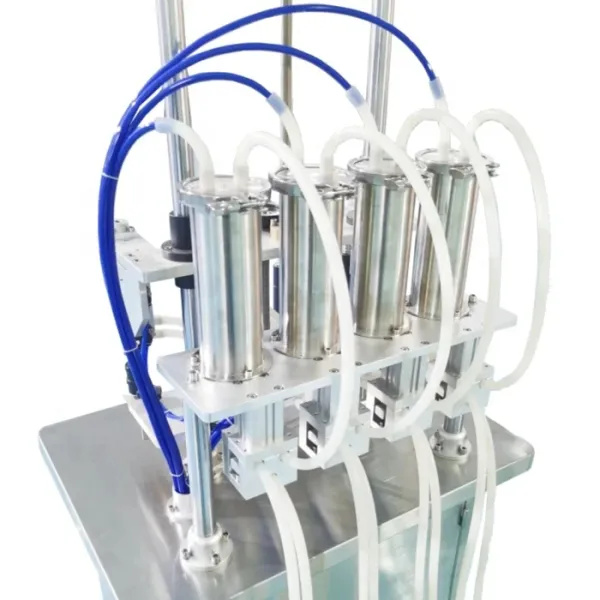
12 Heads Embroidery Machine

Dewatering Pump Machine

Order Collection

Portable Water Drilling Rig

Order Usefully Collected

Batch of Orders

Agriculture Processing Machines

Meat Grinder Machine

Water Pump Equipment

Packaging Machine and accessories

Fabrics Manufacturing Equipment

Mining Equipments

Food Processing Machine

Batch of Orders

Batch of Orders

Latest Orders Labelled
wheel alignment machines

new arrivals
Pre Orders Offloading

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

26 January 2026

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper Rewinding Machine

latest arrivals

offloading

order success

order collection

order offloading


























