B21, China Town Mall, Midrand
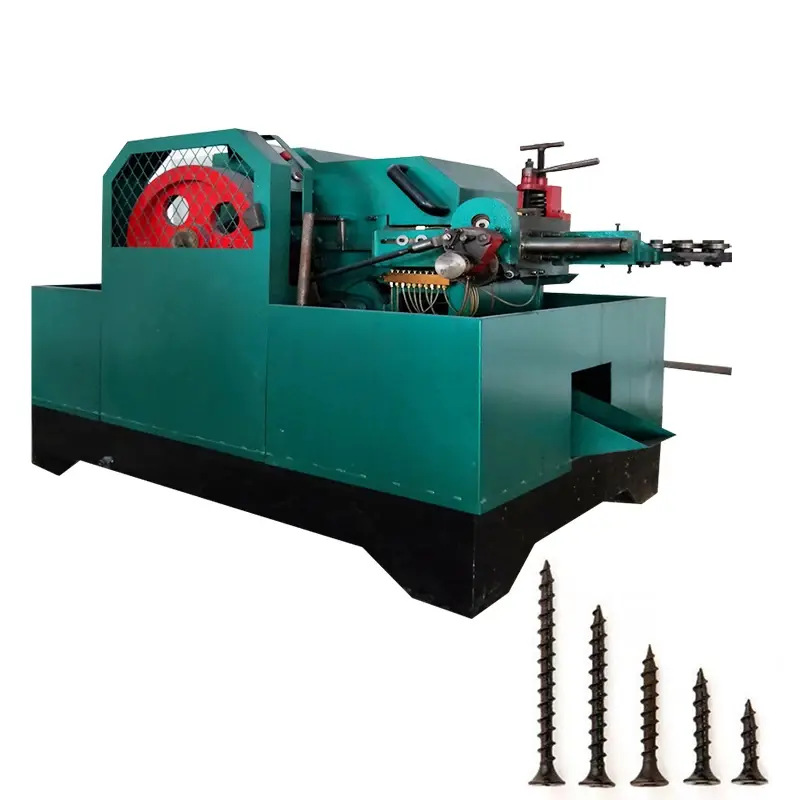
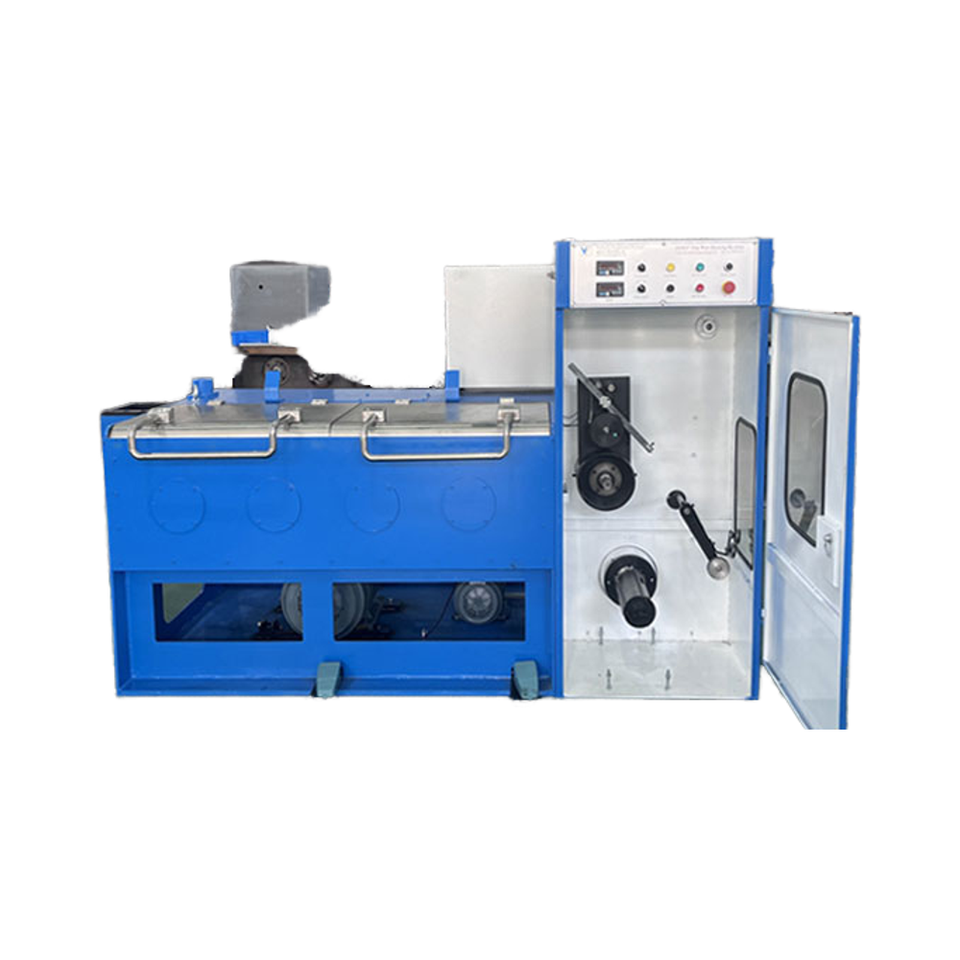
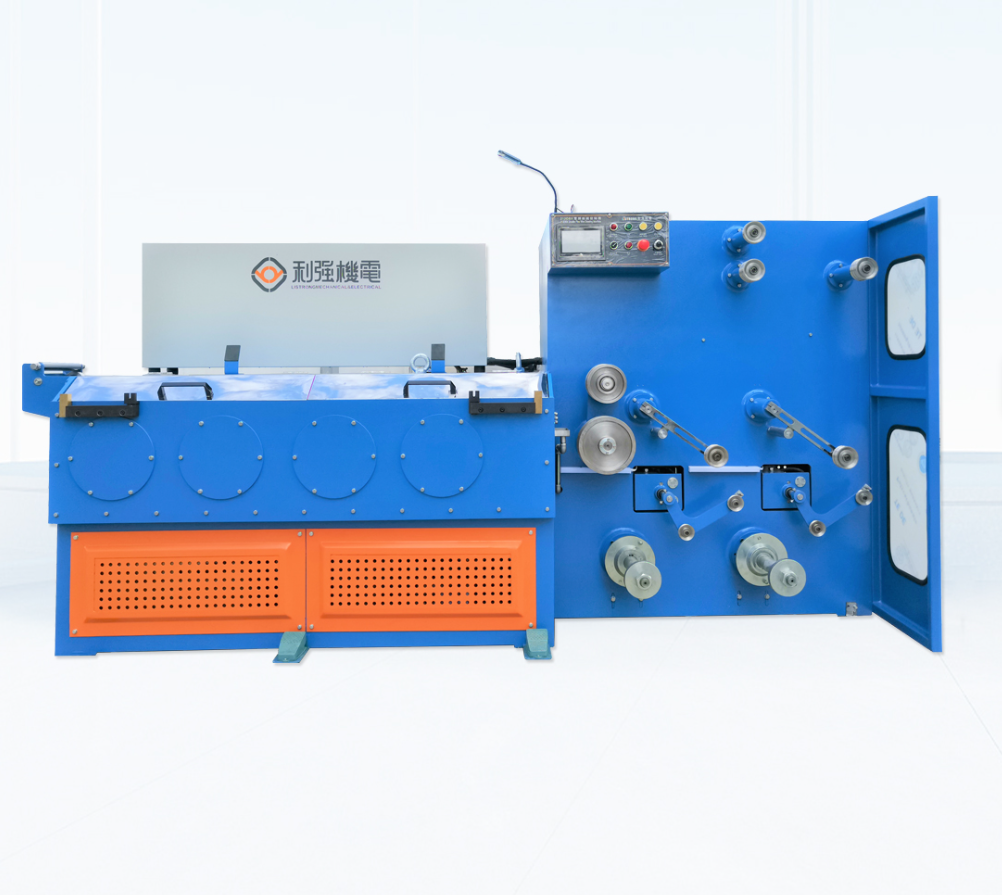
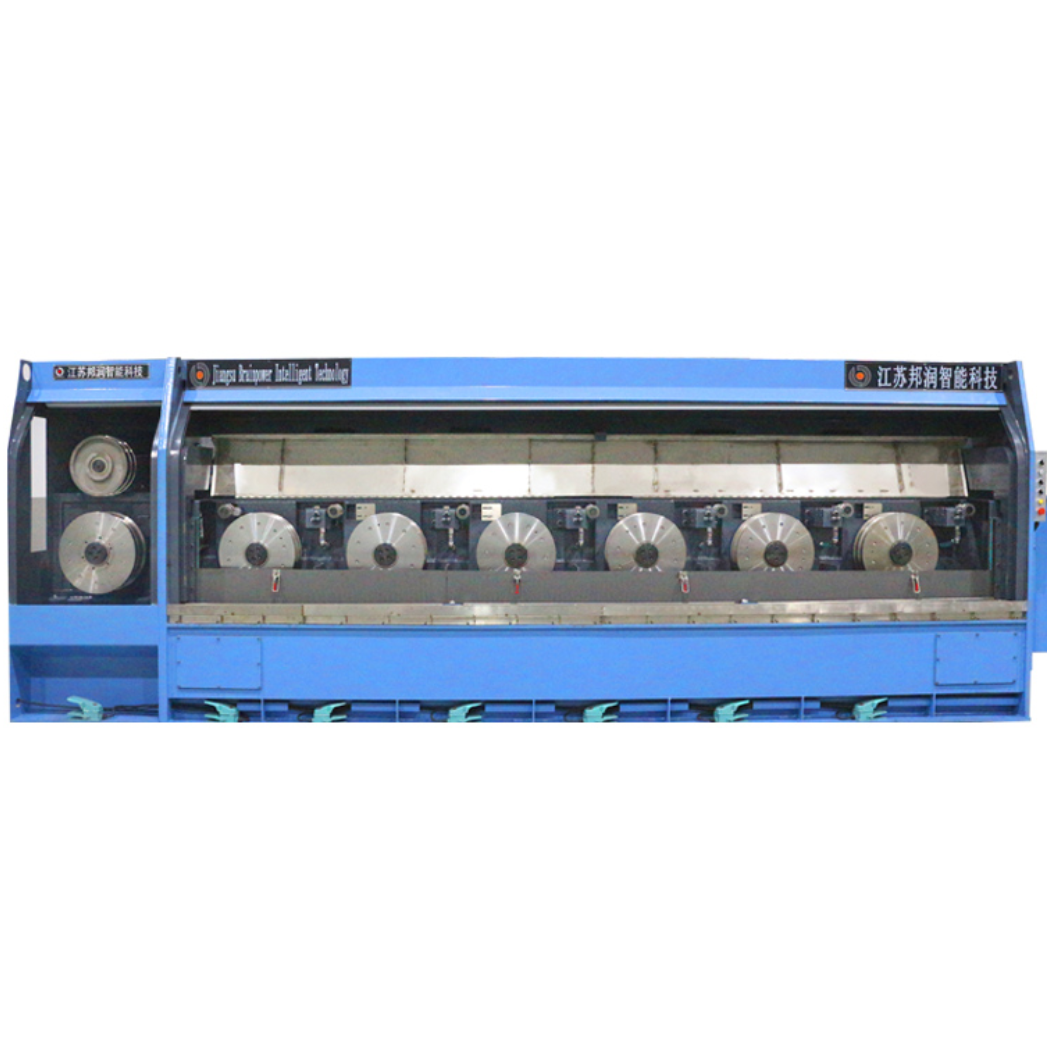
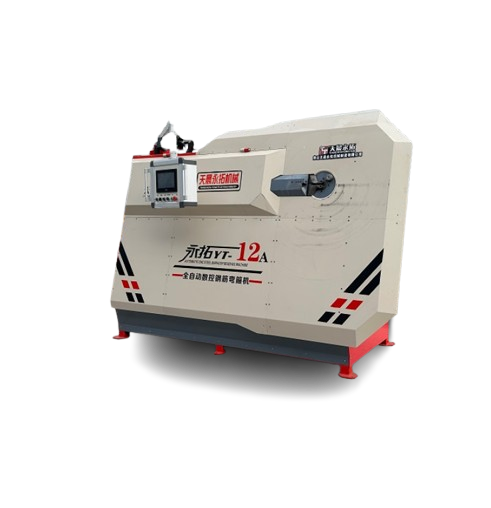
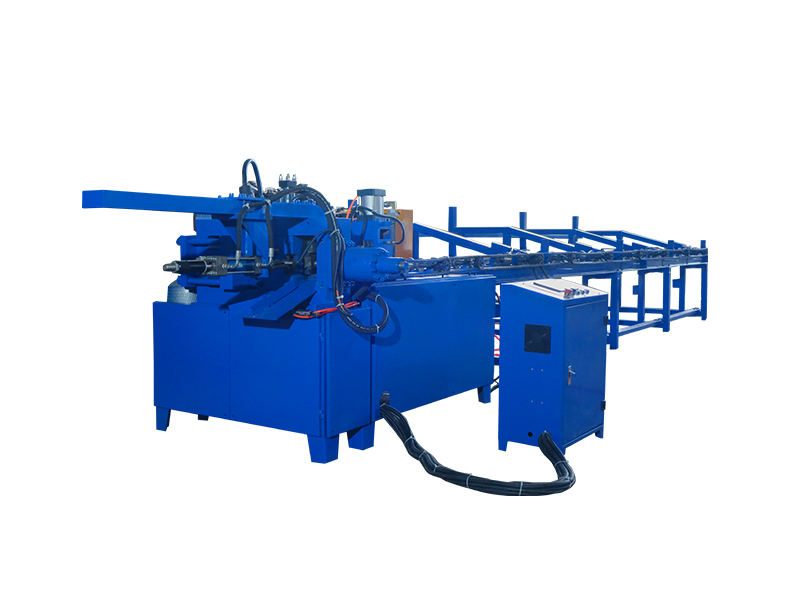
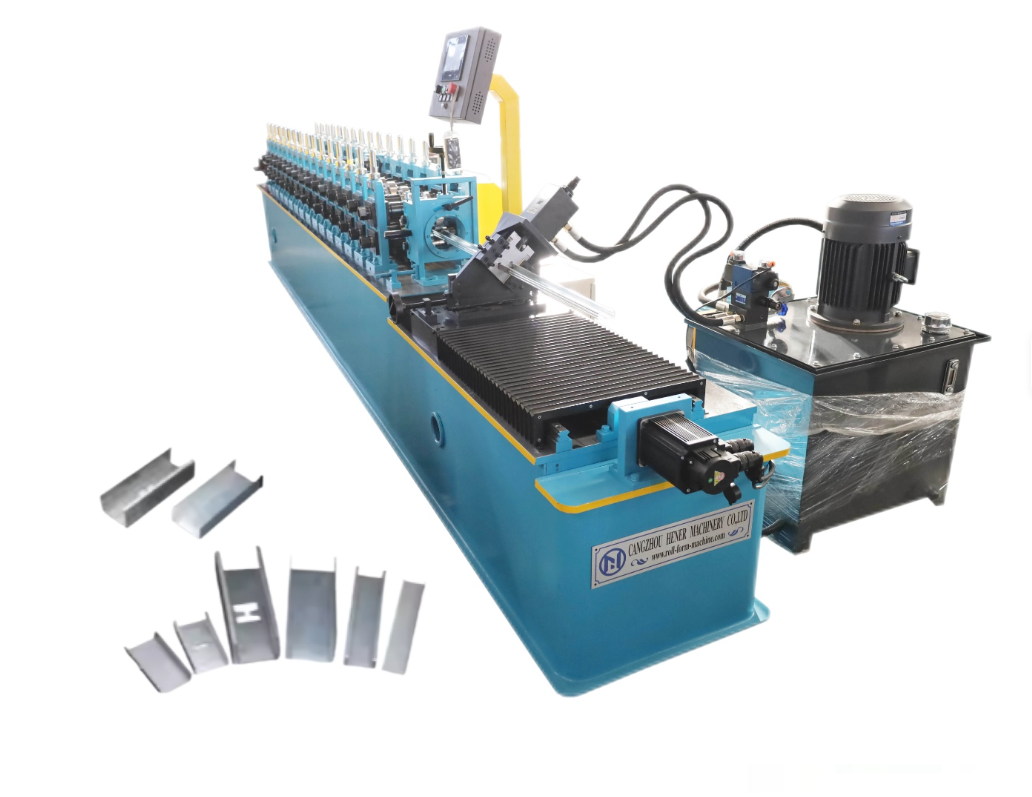
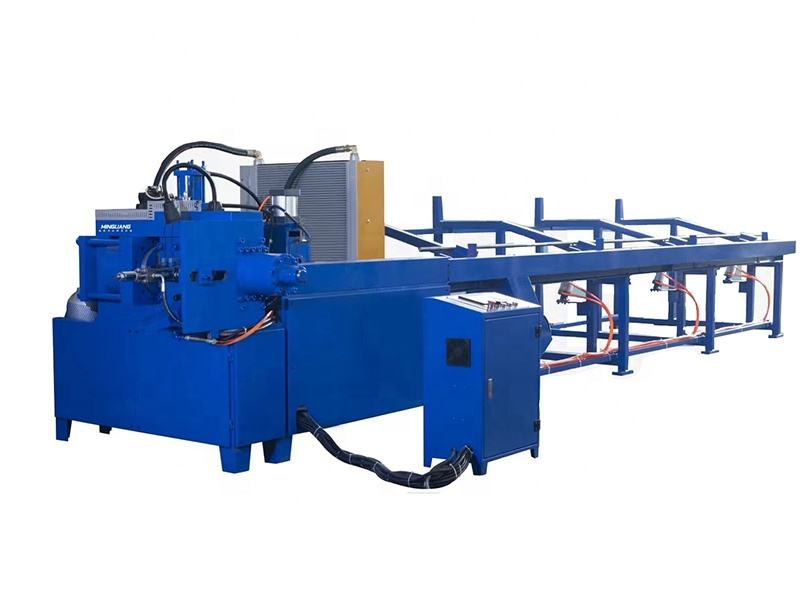
Automatic High-Speed Low-Noise Bolt Nut Screw Making Machines
- Section : Machinery
- Category : Metal & Metallurgy Machinery
- SKU : 1600468762789

- Shipping Timeframes: All orders are processed within 2-5 business days (excluding weekends and holidays). After your order has been processed, the estimated delivery time is before 06 May, 2026, depending on customs, Please note that due to high demand, some items may experience longer shipping times, which will be communicated at order confirmation email.
- Order Processing Time: Please allow 2-5 business days for us to process your order before it is shipped . Orders placed after 16:00 on Fridays, or during weekends and public holidays, will begin processing on the next business day. Processing times may be extended during peak seasons or sales events.
- Manufacturing Time: Some products needs manufacturing time, the manufacturing process will take approximately 10-30 business days depending on the product. This timeframe may vary depending on the complexity of the product and current demand. but this will be communicated with you during order confirmation.
- Returns and Exchanges: We offer a 30-day return policy for most items. If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, you may return it within 30 days of receipt for a refund or exchange. Items must be unused, in their original packaging, and accompanied by proof of purchase. Return shipping costs are the responsibility of the customer, unless the item was damaged or defective upon arrival.
1. What products can the Automatic High-Speed Low-Noise Bolt Nut Screw Making Machines produce?
These systems are designed to produce cold-headed fasteners and rolled-thread parts such as bolts, screws, nuts and similar pin-type parts (often called nails in the spec). Production size capability depends on the selected model and tooling.
2. What are the main machine types and model variants included in this product line?
The product line includes Cold Heading Machines and Thread Rolling Machines with multiple model variants. Cold heading variants cover nail/rod diameters from about 2.0 to 5.0 mm and lengths from 10 to 100 mm, with capacities from ~80 to 180 pcs/min. Thread rolling variants cover diameters roughly 2.0–5.0 mm and lengths 10–100 mm, with capacities up to 280 pcs/min. Motor power options are typically 3 kW or 4 kW depending on model.
3. What are the production speeds (pieces per minute) I can expect?
Cold heading machines in this line typically run from about 80 up to 180 pcs/min depending on model and part geometry. Thread rolling machines can reach up to about 280 pcs/min for smaller parts, with other models in the 100–120 pcs/min range. Actual throughput depends on part size, material and tooling.
4. What diameter and length ranges can these machines handle?
Across the available variants the machines handle wire/rod diameters roughly from 2.0 mm up to 5.0 mm. Finished part lengths shown in the specifications range from about 10 mm up to 100 mm depending on the model.
5. What are the motor power requirements?
Typical motor power for the models shown is 3 kW or 4 kW. Final electrical specifications (voltage, phase, frequency) depend on the chosen configuration—please confirm required supply with the manufacturer or supplier.
6. What are the machine dimensions and weights?
Dimensions vary by model. Examples from the spec: Cold heading models include footprints such as 1.7×1.0×1.0 m (≈1000 kg), 2.0×1.0×1.0 m (≈1700 kg), 1.9×1.2×1.2 m (≈1700 kg) and 2.1×1.2×1.2 m (≈1900 kg). Thread rolling examples include 2.0×1.2×1.4 m (≈1000 kg) and 2.0×1.5×1.3 m (≈1500 kg).
7. The product is described as "low-noise"—what noise levels should I expect?
The machines are engineered for reduced operating noise compared with older designs, but exact dB(A) levels vary by model, tooling and factory layout. If you need measured sound-pressure levels for compliance, request the manufacturer’s noise test report or arrange on-site measurement.
8. What materials (wire/rod types) are compatible?
These cold-heading and thread-rolling machines are generally compatible with common fastener materials such as low-carbon steel, medium-carbon steel, stainless steels and some non-ferrous wires (brass, copper). Compatibility with specific alloys or pre-treated wire should be confirmed with the supplier and may require different tooling or process settings.
9. What level of automation and operator involvement is required?
The machines are automatic and intended for high-speed production. An operator is typically required for feeding/setup, tooling changes, monitoring operations and quality checks. Additional automation (feeders, part conveyors, sorting/inspection) can often be integrated on request.
10. How are tooling and die changes handled and are spare tool sets available?
Tooling (headers, dies, rollers) is specific to part size and geometry. Tool changes are required for size changeovers; changeover time depends on the model and the operator’s experience. Spare tooling and complete die sets are normally available—discuss lead times and pricing with the supplier and consider keeping essential spares on hand.
11. What basic site and installation requirements should I prepare for?
Prepare a level, vibration-resistant concrete floor and sufficient clear space for the machine footprint plus operator access. Ensure stable electrical supply sized for the motor rating (confirm voltage/phase with supplier). Some installations may require foundations or anchoring; the supplier can provide installation instructions and recommend site preparation details.
12. What routine maintenance is required to keep the machines running reliably?
Routine maintenance typically includes daily cleaning of chips and lubricant residues, inspection and lubrication of moving parts, checking and replacing worn dies/rollers, verifying alignment, and periodic inspection of electrical and pneumatic components. Follow the supplier’s maintenance schedule and keep a log of service actions.
13. Are spare parts, technical support and operator training available?
Most suppliers provide spare parts, technical support and optional on-site or remote training for operators and maintenance personnel. Confirm the scope, costs and response times with your chosen supplier prior to purchase.
14. Can these machines be customized for special fastener geometries or integrated into an existing production line?
Yes—manufacturers commonly offer customization for part geometry, special tooling, additional automation (feeders, conveyors, inspection), and control integration to match existing production lines. Provide part drawings and production requirements so the supplier can propose a tailored solution.
15. What are the warranty, delivery and packaging terms?
Warranty, delivery lead-time and packaging/crating vary by supplier and order. Typical factory machines come with a limited warranty period and are shipped crated for export. Ask the supplier for a written quotation that includes warranty terms, lead times, shipping method and packaging details.
Latest Order Arrivals
Discover our latest orders
12 Heads Embroidery Machine

Dewatering Pump Machine

Order Collection

Portable Water Drilling Rig

Order Usefully Collected

Batch of Orders

Agriculture Processing Machines

Meat Grinder Machine

Water Pump Equipment

Packaging Machine and accessories

Fabrics Manufacturing Equipment

Mining Equipments

Food Processing Machine

Batch of Orders

Batch of Orders

Latest Orders Labelled
wheel alignment machines

new arrivals
Pre Orders Offloading

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

26 January 2026

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper Rewinding Machine

latest arrivals

offloading

order success

order collection

order offloading

















